Colorectal Cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer deaths in the United States. Approximately 56,290 people died from colorectal cancer, and 145,290 people were newly diagnosed with the disease in 2005. Colorectal cancer is usually found in people ages 50 and older. Therefore, screening for colorectal cancer for people ages 50 and older is strongly recommended.
Fortunately, Colorectal cancers are some of the most preventable cancers because screening tests can detect growths before they become cancerous. Most colorectal cancers develop from polyps (growths on the lining of the colon). Polyps are usually noncancerous when they first appear. But they can turn into cancerous polyps (adenoma). Removal of these polyps can reduce risk of colon cancer by more than 80 percent.
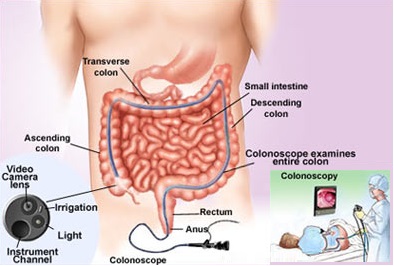
Colon cancer most commonly occurs in the lower part of the colon. Cancer in the rectum is called rectal cancer. Together, they are referred to as colorectal cancer.
Colon cancer happens when cells that are not normal grow in your colon. These cells grow together and form tumors. Colonoscopy is the only colorectal screening test that examines the entire colon and can remove any polyps found during the test. There are other colorectal cancer screening tools, but colonoscopy is the gold standard.
Colorectal Cancer Screening ICD-9-CM diagnosis code for an average risk patient presenting for colonoscopy is:
V76.51 Special Screening for Malignant Neoplasm, Colon
Code V76.51 should be the first listed diagnosis code if the reason for the visit is specifically for the screening exam. For high risk patients, the appropriate family or personal history V code identifying the risk should also be assigned. As with screening for malignant neoplasm of the breast, if a condition is discovered during the screening then the code for the condition may also be assigned as an additional diagnosis.
If the colonoscopy is performed because the patient has a sign or symptom, the sign or symptom code is used to explain the reason for the test, not the screening code. However, if positive findings are discovered during the diagnostic colonoscopy assign the code for these findings instead.
Colorectal cancer screening tests and procedures can be used alone or in various combinations and include fecal blood test, barium enema, flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy. Colonoscopy screening procedures are discussed here.
HCPCS Level ll codes G0105 and G0121 should be reported for Medicare outpatients requiring screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer:
If an abnormality is found during a screening colonoscopy and results in a therapeutic procedure, then the appropriate diagnostic colonoscopy CPT code (45379-45392) is used instead of codes G0105, G0121 or 45378. Therapeutic procedures include biopsy, polypectomy, etc.
Review the CCS Prep column titled, "Understanding How to Code Colonoscopies" for instructions on coding therapeutic procedures.
Example: A patient is seen in the outpatient clinic for screening colonoscopy due to family history of colon cancer. The colonoscopy revealed a colonic polyp that was removed by snare technique. Assign CPT code 45385.
For Medicare OPPS coding, when a screening colonoscopy is attempted but due to extenuating circumstances cannot be completed, code G0105 or G0121 should be reported with either modifier -73 or -74 as appropriate.
Fortunately, Colorectal cancers are some of the most preventable cancers because screening tests can detect growths before they become cancerous. Most colorectal cancers develop from polyps (growths on the lining of the colon). Polyps are usually noncancerous when they first appear. But they can turn into cancerous polyps (adenoma). Removal of these polyps can reduce risk of colon cancer by more than 80 percent.
Colon cancer most commonly occurs in the lower part of the colon. Cancer in the rectum is called rectal cancer. Together, they are referred to as colorectal cancer.
Colon cancer happens when cells that are not normal grow in your colon. These cells grow together and form tumors. Colonoscopy is the only colorectal screening test that examines the entire colon and can remove any polyps found during the test. There are other colorectal cancer screening tools, but colonoscopy is the gold standard.
Colorectal Cancer Screening ICD 9 for Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is a widely used endoscopic technique used to screen individuals for colorectal cancer. It is very sensitive in detecting colorectal cancers. Colonoscopy is an endoscopic procedure in which a thin tube with a camera at the tip is introduced through the anus till the start of the colon.Colorectal Cancer Screening ICD-9-CM diagnosis code for an average risk patient presenting for colonoscopy is:
V76.51 Special Screening for Malignant Neoplasm, Colon
Code V76.51 should be the first listed diagnosis code if the reason for the visit is specifically for the screening exam. For high risk patients, the appropriate family or personal history V code identifying the risk should also be assigned. As with screening for malignant neoplasm of the breast, if a condition is discovered during the screening then the code for the condition may also be assigned as an additional diagnosis.
If the colonoscopy is performed because the patient has a sign or symptom, the sign or symptom code is used to explain the reason for the test, not the screening code. However, if positive findings are discovered during the diagnostic colonoscopy assign the code for these findings instead.
Colorectal cancer screening tests and procedures can be used alone or in various combinations and include fecal blood test, barium enema, flexible sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy. Colonoscopy screening procedures are discussed here.
Colonoscopy CPT Codes for Colon Cancer Screening
After the patient's bowel has been prepped, the physician inserts the colonoscope-a long, thin, flexible lighted tube-through the anus and advances the scope through the colon past the splenic flexure. The lumen of the colon and rectum is visualized. Most polyps and some cancers can be removed during this procedure. The colonoscope is then withdrawn.HCPCS Level ll codes G0105 and G0121 should be reported for Medicare outpatients requiring screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer:
- G0121 Colorectal cancer screening, colonoscopy on individual not meeting criteria for high risk
- G0105 Colorectal cancer screening, colonoscopy on individual at high risk
- Close relative (sibling, parent or child) who has had colorectal cancer or an adenomatous polyp
- Family history of familial adenomatous polyposis
- Family history of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
- Personal history of adenomatous polyps
- Personal history of colorectal cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis
If an abnormality is found during a screening colonoscopy and results in a therapeutic procedure, then the appropriate diagnostic colonoscopy CPT code (45379-45392) is used instead of codes G0105, G0121 or 45378. Therapeutic procedures include biopsy, polypectomy, etc.
Review the CCS Prep column titled, "Understanding How to Code Colonoscopies" for instructions on coding therapeutic procedures.
Example: A patient is seen in the outpatient clinic for screening colonoscopy due to family history of colon cancer. The colonoscopy revealed a colonic polyp that was removed by snare technique. Assign CPT code 45385.
For Medicare OPPS coding, when a screening colonoscopy is attempted but due to extenuating circumstances cannot be completed, code G0105 or G0121 should be reported with either modifier -73 or -74 as appropriate.






Post a Comment
Webmaster reserves the rights to edit/remove comments that is found irrelevant, offensive, contain profanity, serves as spam or attempts to harbor irrelevant links. Please read our Comments Policy for details.
Click to see the code!
To insert emoticon you must added at least one space before the code.